ToyLearn is a start-up that has developed educational toys for children. The company, registered as an Ohio S-Corp, was founded by David and Jen Funster. ToyLearn will be profitable within the first year and expects a significant increase in sales in the early years.
ToyLearn currently offers three educational toys: NumberToy, LetterToy, and PhonicToy. These toys help children learn numbers, letters, phonics, and math skills while being fun to play with. The company is also working on developing new products.
ToyLearn believes that three factors are crucial to its success. Firstly, it must create engaging and educational toys. Secondly, it must maintain strict financial controls. Lastly, it needs to listen to customer feedback and use it for product improvement.
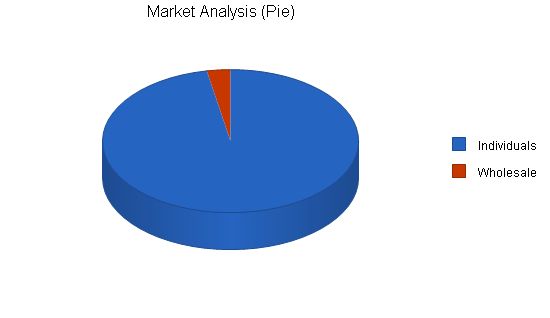
The company has identified two customer segments. The first segment consists of individual customers, such as parents or grandparents, who purchase the toys for their children. This segment is growing at a rate of 8% per year and currently has 3,354,430 potential customers. The second segment includes wholesale purchasers, such as care centers or nursery/preschool organizations, who buy the toys for their clients. This segment is growing at a rate of 10% per year with 702,335 potential customers.
ToyLearn’s success is ensured by its strong management team. David Funster, responsible for product engineering, has an Engineering Degree from the University of Rochester and experience in product development at HP and Nintendo. Jen Funster, with a Masters of Education from Case Western Reserve University, brings expertise in educational tool development.
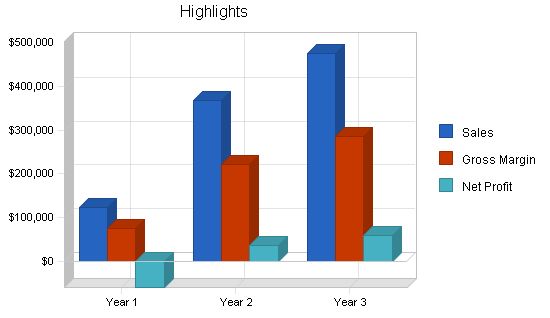
ToyLearn forecasts sales of $367,000 in the second year and $475,000 in the third year. With experienced management, excellent product development, and a promising market opportunity, ToyLearn is poised for success.
1.1 Objectives:
– Create a profitable company.
– Develop innovative, educational toys.
– Improve the learning curve for children through interactive toys.
1.2 Mission:
ToyLearn aims to provide the highest quality educational toys. The more children learn from our toys, the more successful we are.
1.3 Keys to Success:
– Develop creative, educational, engaging toys.
– Implement strict financial controls.
– Listen carefully to customers.
ToyLearn is a start-up that has developed three types of educational toys. The products are fun, engaging, and teach constructive skills. Initially, distribution will focus on the USA, with global distribution being considered.
2.1 Company Ownership:
ToyLearn is a privately held Ohio S-Corp owned by Jen and David Funster.
2.2 Start-up Summary:
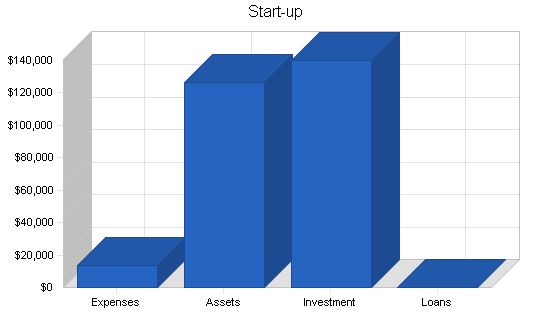
The following items are needed for the start-up:
– Office supplies and equipment for three employees, including desks, computers, and cubicle dividers.
– Prototyping equipment like electric circuit boards, molded plastics, speakers, and LED lights.
– Fax machine, telephones, printers.
Start-up Requirements:
– Legal: $4,000
– Stationery etc.: $200
– Brochures: $200
– Consultants: $3,000
– Insurance: $400
– Rent: $600
– Research and Development: $5,000
– Total Start-up Expenses: $13,400
Start-up Assets:
– Cash Required: $116,600
– Other Current Assets: $0
– Long-term Assets: $10,000
– Total Assets: $126,600
Total Requirements: $140,000
Start-up Funding:
– Start-up Expenses to Fund: $13,400
– Start-up Assets to Fund: $126,600
– Total Funding Required: $140,000
Assets:
– Non-cash Assets from Start-up: $10,000
– Cash Requirements from Start-up: $116,600
– Additional Cash Raised: $0
– Cash Balance on Starting Date: $116,600
– Total Assets: $126,600
Liabilities and Capital:
– Liabilities
– Current Borrowing: $0
– Long-term Liabilities: $0
– Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills): $0
– Other Current Liabilities (interest-free): $0
– Total Liabilities: $0
– Capital
Planned Investment:
– Jen and David: $40,000
– Investor 2: $100,000
– Additional Investment Requirement: $0
– Total Planned Investment: $140,000
Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses): ($13,400)
Total Capital: $126,600
Total Capital and Liabilities: $126,600
Total Funding: $140,000
Products:
ToyLearn has developed three functional and educational toys:
– NumberToy: a toy that emits lights and sounds when children touch a stylus at the appropriate numbers. It teaches number skills and hand-eye coordination.
– LetterToy: similar to NumberToy, it teaches children the alphabet and helps improve attention span.
– PhonicToy: a miniature PC laptop that includes a child’s book and stylus. It reads stories out loud, identifies musical instrument sounds, and guides children in basic addition.
Market Analysis Summary:
The market for educational toys can be divided into two segments:
– Individual consumers: parents or grandparents purchasing toys for a specific child.
– Wholesale purchasers: schools, daycare centers, etc., buying toys for their clients.
ToyLearn sells directly to consumers instead of using wholesalers, which provides better margins but requires more sales generation. Once relationships are established with consumers and wholesale purchasers, marketing costs will decrease.
Market Segmentation:
ToyLearn has segmented the market into two distinct customers:
– Individuals: households with an income of >$50,000, high aspirations for their child’s education and development, and at least an undergraduate degree (41% have a graduate degree).
– Businesses: daycares or schools with 7-25 children that purchase toys for their clients.
Market Analysis:
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5
Potential Customers Growth CAGR
Individuals 8% 3,354,430 3,622,784 3,912,607 4,225,616 4,563,665 8.00%
Wholesale 10% 102,335 112,569 123,826 136,209 149,830 10.00%
Total 8.06% 3,456,765 3,735,353 4,036,433 4,361,825 4,713,495 8.06%
Target Market Segment Strategy:
ToyLearn will focus on individual consumers and wholesale customers for several reasons:
– Better margins. Although sales volume will be less relative to using wholesale distributors, margins will be higher.
– Closer contact with customers. By selling direct to consumers, a stronger relationship will be developed. This is advantageous because it provides a more accurate feedback loop instrumental in product development.
– More efficient. Fewer layers involved in distribution.
The toy industry is characterized by many different toy manufacturers. Within the larger toy industry, there is a niche of educational toy manufacturers. This niche is fairly new (within the last five years) as the convergence of toys and educational tools becomes more legitimized. For years there was no awareness that a toy could have educational value; it was assumed that a toy was a mindless way of occupying a child’s time and attention, giving the parent a break. Only recently have there been studies published that clearly show the ability to design a toy that captivates a child’s attention while teaching them constructive skills.
Competition and Buying Patterns:
The small niche educational toy industry is comprised of two market leaders and several smaller, primarily regional manufacturers. The two main competitors are:
– LeapFrog Enterprises. An Emeryville, CA company. They currently have one main product line that teaches phonic.
– Knowledge Universe. This company was founded by financier Michael Milken and Oracle President Lawrence J. Ellison. Knowledge Universe has a total of seven different products.
In addition, ToyLearn competes with products produced by large game manufacturers.
Strategy and Implementation Summary:
ToyLearn will leverage its two competitive edges (educational and engineering expertise) to produce educational toys that are fun to use and at the same time successful at building important skills for youngsters. By recognizing and exploiting its core competencies, ToyLearn will quickly gain market share and develop a reputation for making effective teaching toys.
Competitive Edge:
ToyLearn has two competitive edges based on their core competencies, education and engineering. Please refer to the Management summary for more detail, but basically ToyLearn will be leveraging what they do best to create a product that is in demand by the market.
To develop good business strategies, perform a SWOT analysis of your business. It’s easy with our free guide and template. Learn how to perform a SWOT analysis.
The marketing strategy will emphasize that ToyLearn’s products are truly educational devices that are fun. This is an important message because parents will want their children to play with this type of toy. The element of “toy” in the product is used to keep the children engaged, something often difficult to do with most educational devices.
The marketing strategy will recognize and account for the fact that there are two distinct customer groups that must be attracted. To capture the awareness of both groups, ToyLearn recognizes that the groups are very different regardless of buying the same product.
ToyLearn will use advertisements and direct mailings. The advertisements will be placed in magazines or journals chosen specifically for the target audience. Magazines will be used for the individuals market and a combination of magazines and journals will be used for the businesses segment.
Sales Strategy:
The sales strategy will be tailored for each customer group. The sales strategy for individuals is to create enough awareness of ToyLearn so that customers are asking their retailers to carry ToyLearn for them. To address the business segment, it is ToyLearn’s goal that the businesses are not just buying one or two of the products but that they are buying all of them addressing different skills, all of which are important. This is especially important as businesses are generally repeat customers. If the customer is happy with the product, it is more than likely that they will become a long-term customer and not look for new vendors.
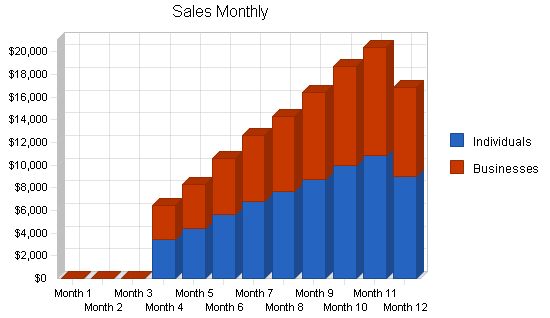
The first three months will not see any sales as the organization will be ramping up production and establishing sales channels. The first year is forecasted to have a fairly slow sales forecast because ToyLearn is a start-up organization. Growth for year two and three should be fairly steep. After year four, it is forecasted that growth will continue, but at a more sustainable rate than during the second and third year.
Sales Forecast
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3
Sales
Individuals $66,580 $196,554 $254,332
Businesses $57,925 $171,002 $221,269
Total Sales $124,505 $367,556 $475,601
Direct Cost of Sales
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3
Individuals $26,632 $78,622 $101,733
Businesses $23,170 $68,401 $88,508
Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales $49,802 $147,022 $190,240
5.4 Milestones
– Business plan completion
– First prototype complete
– First standard production run
– Monthly sales over $10,000
– Profitability
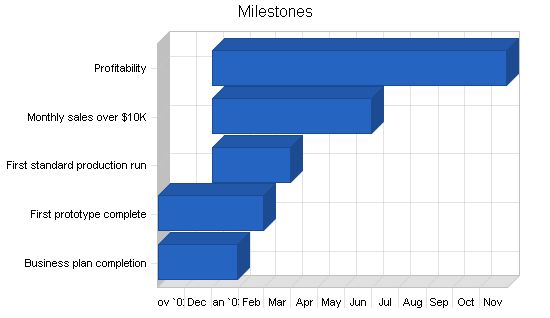
Milestones:
– Business plan completion: 11/1/2002 – 1/30/2003, $0 budget, Jen & David (Manager, Management)
– First prototype complete: 11/1/2002 – 2/28/2003, $0 budget, David (Manager, Engineering)
– First standard production run: 1/1/2003 – 3/30/2003, $0 budget, David (Manager, Engineering)
– Monthly sales over $10K: 1/1/2003 – 6/30/2003, $0 budget, Jen (Manager, Marketing)
– Profitability: 1/1/2003 – 11/30/2003, $0 budget, Jen & David (Manager, Management)
– Totals: $0 budget
5.5 Operations Strategy:
ToyLearn will outsource the manufacture of its products. Jen and David chose outsourcing for several reasons:
1. They lack manufacturing operations/supply chain experience.
2. Outsourcing reduces overhead costs and makes production costs variable.
3. Outsourcing enables the management team to focus on marketing and new product development.
4. It reduces financial risks by avoiding the expense of a manufacturing facility.
5. It increases the scalability of the business model.
Web Plan Summary:
ToyLearn’s website will serve as the primary marketing tool for distributing its products. The website will have two sections: one for general information and a second for retailers/distributors. The second section will include additional information such as inventory.
6.1 Website Marketing Strategy:
The website marketing strategy is simple: include the URL on all printed material and reference it in communications with customers. ToyLearn will also submit the site to various search engines to ensure maximum exposure.
6.2 Development Requirements:
The website will be developed by programmers who were found through David’s personal contacts. It is expected to take one month to build and test the site after the architecture is developed. The site will be continuously monitored for traffic, sales, and usage patterns. Additional development will be performed as needed.
Management Summary:
ToyLearn is founded and operated by David and Jen Funster. They both bring valuable skills to the venture.
– David: Engineering Degree from the University of Rochester. Worked at HP on product development, then Nintendo on handheld game development. Spent four years at Nintendo and saved money for their own company.
– Jen: Provides marketing, product development, and operations insight.
Overall, they recognized their combined skills in developing learning toys and decided to start their own company. Jen’s design insight and David’s prototyping and schematic development were key contributions.
7.1 Personnel Plan:
– Jen: marketing, product development, and operations.
– David: product development and engineering.
– Sales.
– Customer service: this position will also assist with bookkeeping.
Personnel Plan:
– Jen: Year 1 – $24,000, Year 2 – $30,000, Year 3 – $40,000.
– David: Year 1 – $24,000, Year 2 – $30,000, Year 3 – $40,000.
– Sales: Year 1 – $25,000, Year 2 – $34,000, Year 3 – $38,000.
– Customer Service: Year 1 – $25,000, Year 2 – $34,000, Year 3 – $38,000.
– Total People: Year 1 – 4, Year 2 – 4, Year 3 – 0.
– Total Payroll: Year 1 – $98,000, Year 2 – $128,000, Year 3 – $156,000.
This section will provide important financial information.
8.1 Important Assumptions:
Below are the key financial assumptions.
– Plan Month: Year 1 – 1, Year 2 – 2, Year 3 – 3.
– Current Interest Rate: 10.00%.
– Long-term Interest Rate: 10.00%.
– Tax Rate: 30.00%.
– Other: $0.
8.2 Break-even Analysis:
The Break-even Analysis shows that monthly revenue of $30,290 is needed to reach the break-even point.
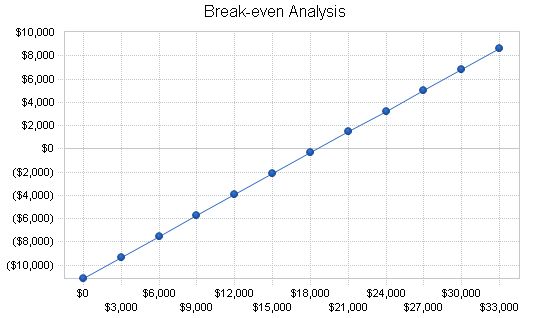
Break-even Analysis
Monthly Revenue Break-even: $18,596
Assumptions:
– Average Percent Variable Cost: 40%
– Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost: $11,158
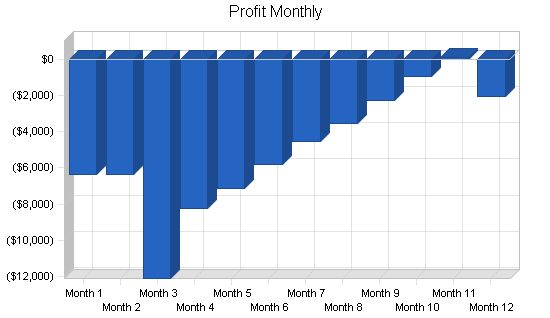
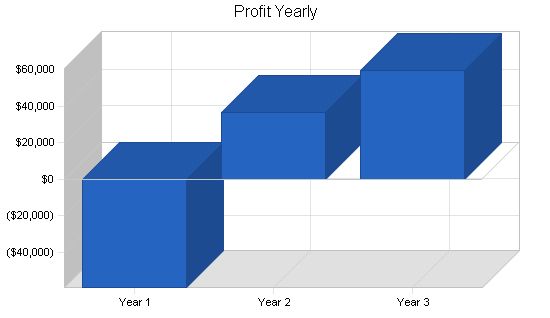
8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
The table and charts below show the projected profit and loss.
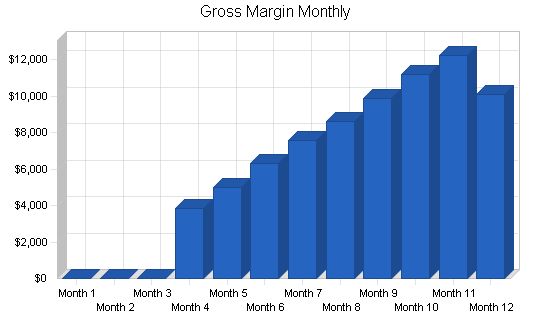
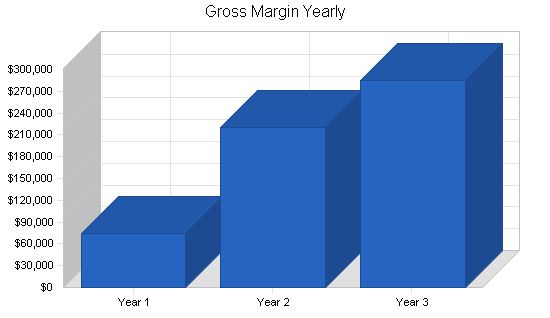
Pro Forma Profit and Loss:
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $124,505 | $367,556 | $475,601 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $49,802 | $147,022 | $190,240 |
| Other Costs of Goods | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $49,802 | $147,022 | $190,240 |
| Gross Margin | $74,703 | $220,534 | $285,361 |
| Gross Margin % | 60.00% | 60.00% | 60.00% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $98,000 | $128,000 | $156,000 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $4,200 | $4,200 | $4,200 |
| Depreciation | $1,992 | $1,992 | $1,992 |
| Rent | $7,200 | $7,200 | $7,200 |
| Utilities | $3,600 | $3,600 | $3,600 |
| Insurance | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Payroll Taxes | $14,700 | $19,200 | $23,400 |
| Other | $1,200 | $1,200 | $1,200 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $133,892 | $168,392 | $200,592 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($59,189) | $52,142 | $84,769 |
| EBITDA | ($57,197) | $54,134 | $86,761 |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Taxes Incurred | $0 | $15,642 | $25,431 |
| Net Profit | ($59,189) | $36,499 | $59,338 |
| Net Profit/Sales | -47.54% | 9.93% | 12.48% |
8.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following table and chart will indicate Projected Cash Flow.
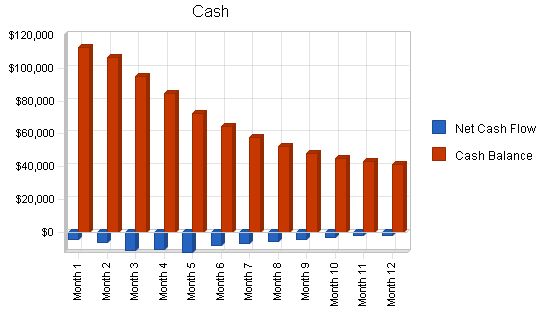
Pro Forma Cash Flow
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Sales | $31,126 | $91,889 | $118,900 |
| Cash from Receivables | $66,011 | $222,242 | $332,951 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $97,137 | $314,131 | $451,852 |
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $97,137 | $314,131 | $451,852 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $98,000 | $128,000 | $156,000 |
| Bill Payments | $74,351 | $193,890 | $253,569 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $172,351 | $321,890 | $409,569 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $172,351 | $321,890 | $409,569 |
| Net Cash Flow | ($75,213) | ($7,759) | $42,283 |
| Cash Balance | $41,387 | $33,628 | $75,911 |
Projected Balance Sheet
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash | $41,387 | $33,628 | $75,911 |
| Accounts Receivable | $27,367 | $80,792 | $104,541 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $68,754 | $114,420 | $180,452 |
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $1,992 | $3,984 | $5,976 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $8,008 | $6,016 | $4,024 |
| Total Assets | $76,762 | $120,436 | $184,476 |
| Accounts Payable | $9,351 | $16,526 | $21,228 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $9,351 | $16,526 | $21,228 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $9,351 | $16,526 | $21,228 |
| Paid-in Capital | $140,000 | $140,000 | $140,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($13,400) | ($72,589) | ($36,090) |
| Earnings | ($59,189) | $36,499 | $59,338 |
| Total Capital | $67,411 | $103,910 | $163,248 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $76,762 | $120,436 | $184,476 |
| Net Worth | $67,411 | $103,910 | $163,248 |
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 195.21% | 29.40% | 3.34% |
| Percent of Total Assets | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 |
| Accounts Receivable | 35.65% | 67.08% | 56.67% | 16.20% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 23.64% |
| Total Current Assets | 89.57% | 95.00% | 97.82% | 79.15% |
| Long-term Assets | 10.43% | 5.00% | 2.18% | 20.85% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile |
| Accounts Payable | 12.18% | 13.72% | 11.51% | 36.32% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 15.56% |
| Total Liabilities | 12.18% | 13.72% | 11.51% | 51.88% |
| Net Worth | 87.82% | 86.28% | 88.49% | 48.12% |
| Percent of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 |
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 60.00% | 60.00% | 60.00% | 34.87% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 107.54% | 50.07% | 47.52% | 22.04% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.89% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | -47.54% | 14.19% | 17.82% | 1.46% |
| Main Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 |
| Current | 7.35 | 6.92 | 8.50 | 1.95 |
| Quick | 7.35 | 6.92 | 8.50 | 0.75 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 12.18% | 13.72% | 11.51% | 59.08% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | -87.80% | 50.18% | 51.93% | 3.36% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | -77.11% | 43.29% | 45.95% | 8.20% |
| Net Profit Margin | -47.54% | 9.93% | 12.48% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | -87.80% | 35.13% | 36.35% | n.a |
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 3.41 | 3.41 | 3.41 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 56 | 72 | 95 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 8.95 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 23 | 27 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 1.62 | 3.05 | 2.58 | n.a |
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.13 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | n.a |
| Net Working Capital | $59,403 | $97,894 | $159,224 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Assets to Sales | 0.62 | 0.33 | 0.39 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 12% | 14% | 12% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 4.43 | 2.03 | 3.58 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 1.85 | 3.54 | 2.91 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
Appendix
Sales Forecast
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 |
General Assumptions: Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Plan Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Current Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Long-term Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Tax Rate 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% Other 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Pro Forma Profit and Loss: Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sales $0 $0 $0 $6,418 $8,329 $10,556 $12,630 $14,317 $16,411 $18,676 $20,359 $16,809 Direct Cost of Sales $0 $0 $0 $2,567 $3,332 $4,222 $5,052 $5,727 $6,564 $7,470 $8,143 $6,724 Other Costs of Goods $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 Total Cost of Sales $0 $0 $0 $2,567 $3,332 $4,222 $5,052 $5,727 $6,564 $7,470 $8,143 $6,724 Gross Margin $0 $0 $0 $3,851 $4,997 $6,334 $7,578 $8,590 $9,847 $11,205 $12,215 $10,086 Gross Margin % 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% 60.00% Expenses Payroll $4,000 $4,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 $9,000 Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 Depreciation $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 $166 Rent $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 Utilities $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 Insurance $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 $250 Payroll Taxes 15% $600 $600 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 $1,350 Other $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 Total Operating Expenses $6,366 $6,366 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 $12,116 Profit Before Interest and Taxes ($6,366) ($6,366) ($12,116) ($8,265) ($7,119) ($5,782) ($4,538) ($3,526) ($2,269) ($911) $99 ($2,030) EBITDA ($6,200) ($6,200) ($11,950) ($8,099) ($6,953) ($5,616) ($4,372) ($3,360) ($2,103) ($745) $265 ($1,864) Interest Expense $0 $0 $0 $0 Pro Forma Cash Flow |
|||||||
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | $1,604 | $2,082 | $2,639 | $3,157 | $3,579 | $4,103 | $4,669 | $5,090 | $4,202 | ||||
| Cash from Receivables | $160 | $4,861 | $6,302 | $7,969 | $9,515 | $10,790 | $12,365 | $14,049 | |||||
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $1,604 | $2,243 | $7,500 | $9,460 | $11,548 | $13,617 | $15,459 | $17,455 | $18,251 | ||||
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ||
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ||
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ||
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ||
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ||
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ||
| Subtotal Cash Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $1,604 | $2,243 | $7,500 | $9,460 | $11,548 | $13,617 | $15,459 | $17,455 | $18,251 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $116,600 | $112,527 | $106,327 | $95,102 | $84,671 | $72,371 | $64,560 | $57,819 | $52,343 | $48,256 | $45,170 | $43,182 | $41,387 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $4,813 | $10,900 | $13,956 | $17,126 | $19,894 | $22,688 | $25,905 | $28,809 | $27,367 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $116,600 | $112,527 | $106,327 | $95,102 | $89,484 | $83,270 | $78,515 | $74,945 | $72,237 | $70,944 | $71,075 | $71,991 | $68,754 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $9,834 | $9,668 | $9,502 | $9,336 | $9,170 | $9,004 | $8,838 | $8,672 | $8,506 | $8,340 | $8,174 | $8,008 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $9,834 | $9,668 | $9,502 | $9,336 | $9,170 | $9,004 | $8,838 | $8,672 | $8,506 | $8,340 | $8,174 | $8,008 |
| Total Assets | $126,600 | $122,361 | $115,995 | $104,604 | $98,820 | $92,440 | $87,519 | $83,783 | $80,909 | $79,450 | $79,415 | $80,165 | $76,762 |
Hello!
I’m Andrew Brooks, a seasoned finance consultant from the USA and the mind behind phonenumber247.com.
My career is built on a foundation of helping individuals and businesses thrive financially in an ever-changing economic landscape. At phonenumber247.com, my aim is to demystify the complex world of finance, providing clear, actionable advice that can help you navigate your financial journey with confidence. Whether it’s personal finance management, investment strategies, or understanding the nuances of market dynamics, I’m here to share insights and tools that can propel you towards your financial goals.
Welcome to my digital space, where every piece of advice is a step closer to financial clarity and success!
