Contents
Construction Repair Business Plan
HodgePodge Sealcoating Company offers crack filling and sealcoating to residential customers. Sealcoating protects asphalt driveways by filling cracks and coating the surface, protecting it against the elements. HodgePodge will leverage their industry-benchmarked customer service to rapidly gain market share.
Although HodgePodge is a seasonal business, operating for eight months, they will maintain an office/garage year round in a low rent facility in an industrial district. Even operating seasonally, HodgePodge will reach profitability by month seven and achieve respectable profits by the end of year three.
1.1 Objectives
The first three years of operation objectives:
- Create a service-based company that exceeds customer’s expectations.
- Increase the number of clients by 20% per year through superior service.
- Develop a sustainable start-up business, surviving off its own cash flow.
1.2 Keys to Success
To provide a reasonably priced sealcoating job that exceeds customer’s expectations. Sealcoating business does not have outstanding customer service.
1.3 Mission
HodgePodge Sealcoating Company’s mission is to provide customers with the finest level of service available in the industry. We exist to attract and maintain customers. When we adhere to this maxim, everything else will fall into place. Our services will exceed customer expectations.
Company Summary
HodgePodge Sealcoating Company, based in Washington, PA, is a sealcoating company that serves the residential market. HodgePodge will use a garage with an attached room for storage and office space. The truck and raw materials will also be stored here. The office is a small room.
HodgePodge is a seasonal business as sealcoat cannot be applied in cold or wet conditions. The garage/office is located in an industrial area to lower rental cost during the off-season.
2.1 Company Ownership
HodgePodge is owned and operated by Dan Slopster.
2.2 Start-up Summary
HodgePodge will incur the following start-up costs:
- Computer system with CD-RW, printer, Microsoft Office, QuickBooks Pro, and Internet connection.
- Desk, chair, file cabinet, and cellular phone.
- Pickup truck and gasoline leaf blower.
- Sealcoating mixer and hot crack filler mixer.
- Squeegees for sealcoat and crack filler application.
- Containers for raw ingredient storage and sand (for filling cracks larger than 1/8th inch in depth).
- Work clothing and water container.
Some items are considered long-term assets and will be depreciated using G.A.A.P. approved straight-line depreciation method.
Start-up
Requirements
– Legal: $200
– Stationery etc.: $200
– Brochures: $0
– Consultants: $0
– Insurance: $0
– Rent: $0
– Research and Development: $0
– Expensed Equipment: $0
– Other: $0
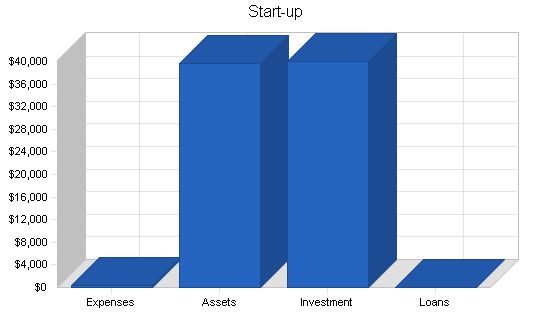
– Total Start-up Expenses: $400
Start-up Assets
– Cash Required: $28,800
– Other Current Assets: $0
– Long-term Assets: $10,800
– Total Assets: $39,600
Total Requirements: $40,000
Start-up Funding
– Start-up Expenses to Fund: $400
– Start-up Assets to Fund: $39,600
– Total Funding Required: $40,000
Assets
– Non-cash Assets from Start-up: $10,800
– Cash Requirements from Start-up: $28,800
– Additional Cash Raised: $0
– Cash Balance on Starting Date: $28,800
– Total Assets: $39,600
Liabilities and Capital
– Liabilities
– Current Borrowing: $0
– Long-term Liabilities: $0
– Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills): $0
– Other Current Liabilities (interest-free): $0
– Total Liabilities: $0
– Capital
– Planned Investment
– Dan: $40,000
– Investor 2: $0
– Other: $0
– Additional Investment Requirement: $0
– Total Planned Investment: $40,000
– Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses): ($400)
– Total Capital: $39,600
Total Capital and Liabilities: $39,600
Total Funding: $40,000
Services
HodgePodge provides residential sealcoating and crack filling. Sealcoating is the process of spreading an asphalt-based product that coats the surface of an asphalt driveway, filling in small cracks and sealing against the elements. Crack filler is applied first to fill in gaps in the driveway. If the crack is more than 1/8th inch deep, sand is added.
Before sealcoating, the driveway must be cleared of debris to ensure adhesion. Once debris is removed, cracks are filled. The sealcoat is then applied and the driveway must dry for 24 hours before use.
The typical cost for sealcoating a driveway ranges from $200-$300 depending on size and condition.
Market Analysis Summary
HodgePodge has identified two distinct segments of the population that consume sealcoating services. HodgePodge will have one marketing campaign that targets both groups.
4.1 Market Segmentation
HodgePodge’s market can be segmented into two groups:
– People with disposable income who can afford to pay for services. This group typically has a household income over $50,000 and pays for maintenance services like lawn care.
– Older people who believe they are not physically capable of doing the work themselves or choose not to. They believe sealcoating is too exerting or messy, especially at their age. They also believe it extends the life of their driveway.
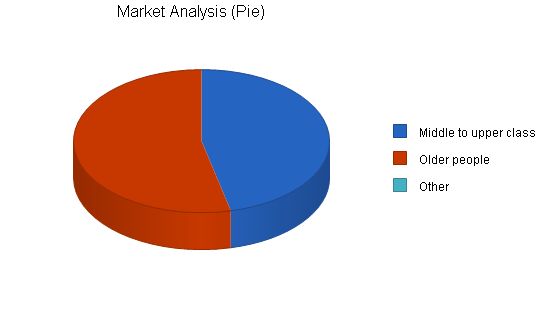
Market Analysis:
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5
Potential Customers
Growth
Middle to upper class 9.00%
18,545 20,214 22,033 24,016 26,177 9.00%
Older people 8.00%
21,455 23,171 25,025 27,027 29,189 8.00%
Other 0.00%
0 0 0 0 0 0.00%
Total 8.47%
40,000 43,385 47,058 51,043 55,366 8.47%
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
HodgePodge’s strategy for reaching these people will be based on advertisements in the local paper’s metro section where service providers advertise. This section is well received by the community and often referred to when looking for a service provider.
Additionally, HodgePodge will have a yellow pages advertisement and leverage word of mouth referrals. Creating an economic incentive for current customers to make referrals will build a loyal customer base.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
The sealcoating business consists primarily of independent contractors, larger paving companies, and a few franchises. Independent contractors make up the bulk of the business.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
The sealcoating industry is composed of independent contractors, as well as two sealcoat-specific companies, Dura-Seal and Sealer King.
Consumers’ buying patterns are typically based on price and perceived customer service, with an emphasis on price. Since there is often little differentiation based on the actual product, price becomes the primary factor. The industry is not known for its stellar customer service.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
HodgePodge will aggressively court new customers by leveraging their competitive advantage of superior customer support. Good customer service is rare in the industry, so HodgePodge will stand out. During initial estimation phases, HodgePodge employees will professionally respond to customer questions and provide a written pamphlet with information about the company, sealcoating, pros and cons, and reasonable expectations.
This initial interaction will demonstrate HodgePodge’s stellar customer service, turning prospective individuals into clients.
5.1 Competitive Edge
HodgePodge’s competitive edge is outstanding customer service. This begins with the initial interaction and continues when the company is on-site. Employees will inform customers about the completed job, curing, expectations, and provide contact information for any problems or questions.
Employees will be specifically trained to interact with customers, serving as HodgePodge’s representatives.
5.2 Sales Strategy
HodgePodge will impress customers with excellent customer service during initial meetings. Competition on price is difficult, so HodgePodge will focus on providing detailed information about sealcoating, advantages and disadvantages, and reasonable expectations. By empowering customers with information, HodgePodge believes they will choose their service.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The first month will be dedicated to setting up the work area and office, with no sales activity. The next month will involve lining up initial customers, hiring, and employee training. By the third month, HodgePodge will begin sealcoating driveways. Business will steadily grow until September when the season winds down. Profitability will be reached by the seventh month.
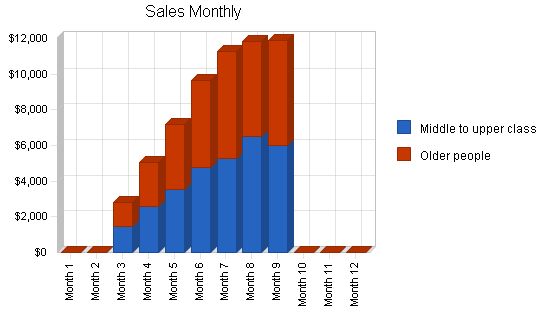
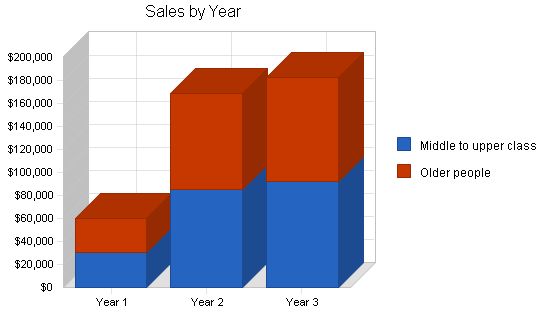
Sales Forecast
| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Middle to upper class | $30,129 | $85,474 | $92,454 |
| Older people | $29,551 | $83,254 | $90,145 |
| Total Sales | $59,680 | $168,728 | $182,599 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Middle to upper class | $3,013 | $8,547 | $9,245 |
| Older people | $2,955 | $8,325 | $9,015 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $5,968 | $16,873 | $18,260 |
5.3 Milestones
HodgePodge will have several early milestones:
- Business plan completion. This will be done as a roadmap for the organization, serving as an indispensable tool for ongoing performance and improvement.
- Office set up.
- Hiring and training three full-time employees.
- Profitability.
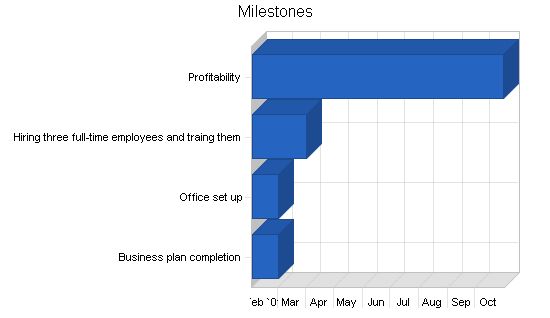
Milestones:
Business plan completion: 2/1/2001 – 3/1/2001, $0 budget, ABC Manager, Marketing Department.
Office set up: 2/1/2001 – 3/1/2001, $0 budget, ABC Manager, Department.
Hiring three full-time employees and training them: 2/1/2001 – 4/1/2001, $0 budget, ABC Manager, Department.
Profitability: 2/1/2001 – 10/31/2001, $0 budget, ABC Manager, Department.
Management Summary:
HodgePodge is owned and operated by Dan Slopster. Dan first learned about sealcoating before starting college. He started his own small sealcoating company where he would sign up neighbors for jobs after sealcoating his parents driveway. Dan handled everything himself, from soliciting the job to completing the work.
During college breaks, Dan would receive calls from old customers asking him to do their driveway. He enjoyed the easy money. After graduating, Dan worked in the Human Resource department of Heinz in Pittsburgh but decided he didn’t want to work for someone else for the rest of his life.
Dan left Heinz, moved to Washington, PA, and explored opportunities as his own boss. After researching the market, he discovered that sealcoating was an attractive industry due to its poor customer service. Dan believed a new company could succeed by prioritizing customer satisfaction.
Personnel Plan:
Dan will work full time for HodgePodge, handling hiring, training, sales, strategic development, and assisting with driveway work for training purposes.
By month three, three full-time employees will be hired and will work with HodgePodge until November, when the sealcoating season ends.
For the second season, an additional crew of three people will be hired.
Table: Personnel Plan
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3
Dan $36,000 $36,000 $36,000
Employee 1 $8,960 $8,960 $8,960
Employee 2 $8,960 $8,960 $8,960
Employee 3 $8,960 $8,960 $8,960
Employee 4 $0 $8,960 $8,960
Employee 5 $0 $8,960 $8,960
Employee 6 $0 $8,960 $8,960
Total People: 1 7 7
Total Payroll: $62,880 $89,760 $89,760
The following sections outline important financial information.
Important Assumptions:
Table: General Assumptions
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3
Plan Month 1 2 3
Current Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00%
Long-term Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00%
Tax Rate 30.00% 30.00% 30.00%
Other 0 0 0
The Break-even Analysis determines the monthly revenue needed to reach the break-even point.
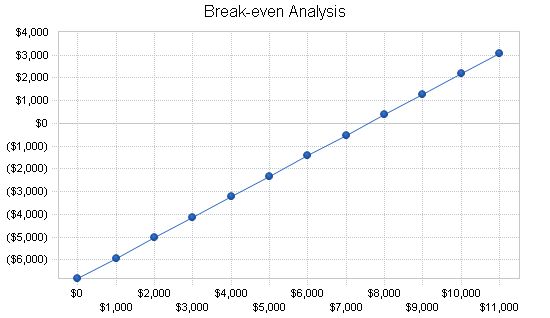
Break-even Analysis:
| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $7,571 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 10% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $6,814 |
7.3 Projected Profit and Loss
Projected profit and loss:
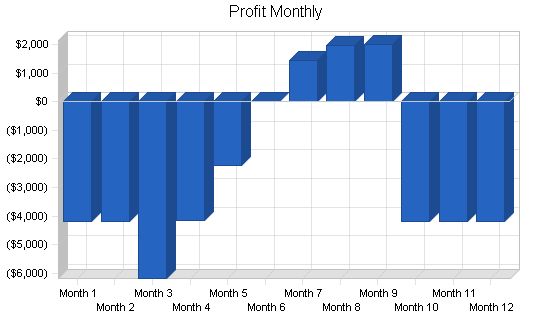
Pro Forma Profit and Loss
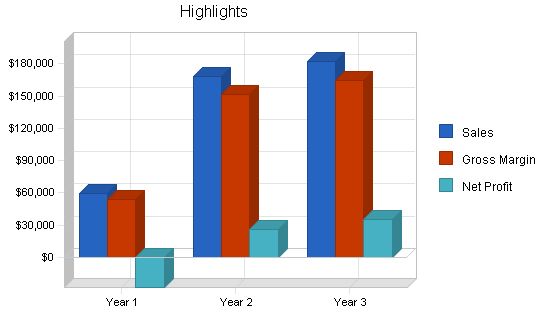
Sales
Year 1: $59,680
Year 2: $168,728
Year 3: $182,599
Direct Cost of Sales
Year 1: $5,968
Year 2: $16,873
Year 3: $18,260
Other Production Expenses
Year 1: $0
Year 2: $0
Year 3: $0
Total Cost of Sales
Year 1: $5,968
Year 2: $16,873
Year 3: $18,260
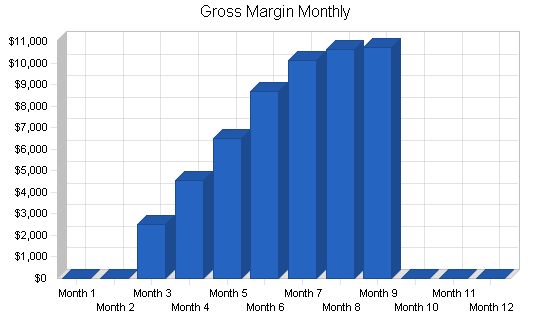
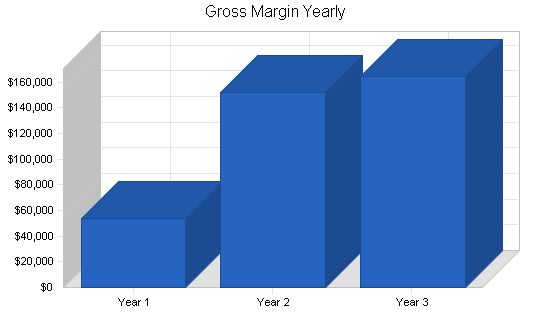
Gross Margin
Year 1: $53,712
Year 2: $151,855
Year 3: $164,339
Gross Margin %
Year 1: 90.00%
Year 2: 90.00%
Year 3: 90.00%
Expenses
Payroll
Year 1: $62,880
Year 2: $89,760
Year 3: $89,760
Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses
Year 1: $700
Year 2: $700
Year 3: $700
Depreciation
Year 1: $2,160
Year 2: $4,260
Year 3: $4,260
Leased Equipment
Year 1: $0
Year 2: $0
Year 3: $0
Utilities
Year 1: $600
Year 2: $600
Year 3: $600
Insurance
Year 1: $1,200
Year 2: $1,200
Year 3: $1,200
Rent
Year 1: $4,800
Year 2: $4,800
Year 3: $4,800
Payroll Taxes
Year 1: $9,432
Year 2: $13,464
Year 3: $13,464
Other
Year 1: $0
Year 2: $0
Year 3: $0
Total Operating Expenses
Year 1: $81,772
Year 2: $114,784
Year 3: $114,784
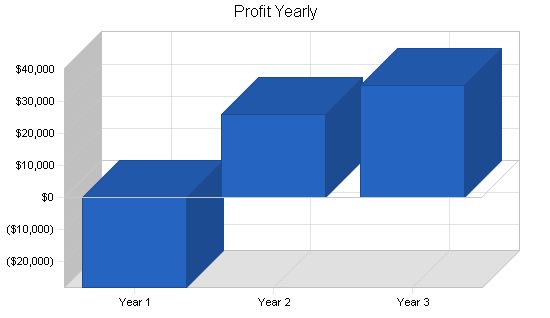
Profit Before Interest and Taxes
Year 1: ($28,060)
Year 2: $37,071
Year 3: $49,555
EBITDA
Year 1: ($25,900)
Year 2: $41,331
Year 3: $53,815
Interest Expense
Year 1: ($65)
Year 2: ($180)
Year 3: ($270)
Taxes Incurred
Year 1: $0
Year 2: $11,175
Year 3: $14,948
Net Profit
Year 1: ($27,995)
Year 2: $26,076
Year 3: $34,878
Net Profit/Sales
Year 1: -46.91%
Year 2: 15.45%
Year 3: 19.10%
7.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table indicate projected cash flow.
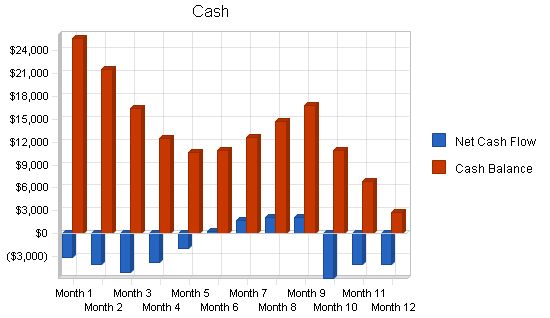
Pro Forma Cash Flow
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $59,680 | $168,728 | $182,599 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $59,680 | $168,728 | $182,599 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $59,680 | $168,728 | $182,599 |
| Expenditures | |||
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $62,880 | $89,760 | $89,760 |
| Bill Payments | $21,678 | $45,592 | $53,285 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $84,558 | $135,352 | $143,045 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $1,200 | $1,200 | $600 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $10,500 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $85,758 | $147,052 | $143,645 |
| Net Cash Flow | ($26,078) | $21,676 | $38,954 |
| Cash Balance | $2,722 | $24,398 | $63,352 |
Projected Balance Sheet
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $2,722 | $24,398 | $63,352 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $2,722 | $24,398 | $63,352 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $10,800 | $21,300 | $21,300 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $2,160 | $6,420 | $10,680 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $8,640 | $14,880 | $10,620 |
| Total Assets | $11,362 | $39,278 | $73,972 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $957 | $3,997 | $4,414 |
| Current Borrowing | ($1,200) | ($2,400) | ($3,000) |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | ($243) | $1,597 | $1,414 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | ($243) | $1,597 | $1,414 |
| Paid-in Capital | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($400) | ($28,395) | ($2,319) |
| Earnings | ($27,995) | $26,076 | $34,878 |
| Total Capital | $11,605 | $37,681 | $72,558 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $11,362 | $39,278 | $73,972 |
| Net Worth | $11,605 | $37,681 | $72,558 |
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 182.72% | 8.22% | 7.50% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 29.80% |
| Total Current Assets | 23.96% | 62.12% | 85.64% | 67.00% |
| Long-term Assets | 76.04% | 37.88% | 14.36% | 33.00% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | ||||
| Accounts Payable | -2.14% | 4.07% | 1.91% | 43.50% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 14.10% |
| Total Liabilities | -2.14% | 4.07% | 1.91% | 57.60% |
| Net Worth | 102.14% | 95.93% | 98.09% | 42.40% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 90.00% | 90.00% | 90.00% | 29.40% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 141.12% | 74.62% | 71.00% | 15.50% |
| Advertising Expenses | 1.21% | 0.41% | 0.38% | 0.30% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | -47.02% | 21.97% | 27.14% | 2.40% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | -11.20 | 15.28 | 44.81 | 1.55 |
| Quick | -11.20 | 15.28 | 44.81 | 1.17 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | -2.14% | 4.07% | 1.91% | 57.60% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | -241.23% | 98.86% | 68.67% | 6.50% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | -246.39% | 94.84% | 67.36% | 15.40% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | -46.91% | 15.45% | 19.10% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | -241.23% | 69.20% | 48.07% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 23.65 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 19 | 29 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 5.25 | 4.30 | 2.47 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | -0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $2,965 | $22,801 | $61,938 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
|
General Assumptions: Plan Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Current Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Long-term Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Tax Rate 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% Other 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Pro Forma Profit and Loss: Sales Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sales $0 $0 $2,801 $5,042 $7,199 $9,660 $11,265 $11,825 $11,888 $0 $0 $0 Direct Cost of Sales $0 $0 $280 $504 $720 $966 $1,127 $1,183 $1,189 $0 $0 $0 Other Production Expenses $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 Total Cost of Sales $0 $0 $280 $504 $720 $966 $1,127 $1,183 $1,189 $0 $0 $0 Gross Margin $0 $0 $2,521 $4,538 $6,479 $8,694 $10,139 $10,643 $10,699 $0 $0 $0 Gross Margin % 0.00% 0.00% 90.00% 90.00% 90.00% 90.00% 90.00% 90.00% 90.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% Expenses Payroll $3,000 $3,000 $6,840 $6,840 $6,840 $6,840 $6,840 $6,840 $6,840 $3,000 $3,000 $3,000 Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses $0 $0 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $0 $0 $0 Depreciation $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 $180 Leased Equipment $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 Utilities $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 $50 Insurance $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 Rent $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 Payroll Taxes 15% $450 $450 $1,026 $1,026 $1,026 $1,026 $1,026 $1,026 $1,026 $1,026 $450 $450 $450 Other $0 $0 $ Pro Forma Balance Sheet: |
||||
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $28,800 | $25,667 | $21,568 | $16,398 | $12,539 | $10,614 | $10,934 | $12,617 | $14,704 | $16,800 | $10,904 | $6,813 | $2,722 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $28,800 | $25,667 | $21,568 | $16,398 | $12,539 | $10,614 | $10,934 | $12,617 | $14,704 | $16,800 | $10,904 | $6,813 | $2,722 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 | $10,800 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $180 | $360 | $540 | $720 | $900 | $1,080 | $1,260 | $1,440 | $1,620 | $1,800 | $1,980 | $2,160 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $10,800 | $10,620 | $10,440 | $10,260 | $10,080 | $9,900 | $9,720 | $9,540 | $9,360 | $9,180 | $9,000 | $8,820 | $8,640 |
| Total Assets | $39,600 | $36,287 | $32,008 | $26,658 | $22,619 | $20,514 | $20,654 | $22,157 | $24,064 | $25,980 | $19,904 | $15,633 | $11,362 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $966 | $965 | $1,888 | $2,104 | $2,312 | $2,549 | $2,703 | $2,757 | $2,762 | $959 | $958 | $957 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | ($100) | ($200) | ($300) | ($400) | ($500) | ($600) | ($700) | ($800) | ($900) | ($1,000) | ($1,100) | ($1,200) |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $866 | $765 | $1,588 | $1,704 | $1,812 | $1,949 | $2,003 | $1,957 | $1,862 | ($41) | ($142) | ($243) |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 | $866 | $765 | $1,588 | $1,704 | $1,812 | $1,949 | $2,003 | $1,957 | $1,862 | ($41) | ($142) | ($243) |
Hello!
I’m Andrew Brooks, a seasoned finance consultant from the USA and the mind behind phonenumber247.com.
My career is built on a foundation of helping individuals and businesses thrive financially in an ever-changing economic landscape. At phonenumber247.com, my aim is to demystify the complex world of finance, providing clear, actionable advice that can help you navigate your financial journey with confidence. Whether it’s personal finance management, investment strategies, or understanding the nuances of market dynamics, I’m here to share insights and tools that can propel you towards your financial goals.
Welcome to my digital space, where every piece of advice is a step closer to financial clarity and success!

