FoodFun Lifeskills Instructional Software (FoodFun LIS) is a start-up organization aiming to create exceptional education/entertainment software for non-reading individuals with developmental disabilities. The software, developed by a Ph.D. veteran in special education, caters to the specific needs of this customer segment. It is designed to be both instructive, teaching essential lifeskills, and enjoyable to encourage frequent use. FoodFun LIS is an Illinois L.L.C. established by founder and owner Sue Altamirankow, Ph.D., located in Chicago.
FoodFun has identified four key market segments that are likely interested in their software product:
1. Centers for Independent Living: These centers focus on training individuals with developmental disabilities to live independently, with an emphasis on four primary lifeskills.
2. School Districts: All states must provide education for students with special needs until age 21. School districts, usually the educational providers until age 18, are interested in FoodFun’s software to help students acquire fundamental lifeskills.
3. Proactive Parents: Parents who actively participate in their children’s education are seeking aids to assist their child’s learning progress at home.
4. Agencies: Many states have established agencies that connect service providers with individuals. These agencies often form as a result of settlements or payouts from lawsuits, including class actions.
Parents typically purchase one copy of the program, while the other segments generally buy multiple copies or site licenses and are likely to purchase upgrades in the future.
The software product focuses on two main lifeskills: grocery shopping and socialization/leisure. FoodFun has developed a unique software that serves as an effective teaching aid for these skills. The grocery shopping component is a digital cookbook, where each recipe is represented by a picture. When the student selects a picture, they see a list of ingredient and utensil pictures needed to make the dish. These pictures can be printed and taken to the grocery store, enabling independent shopping.
The socialization/leisure time module allows users to choose from various social events/parties for which they can prepare food. The module incorporates music related to each social event, providing entertainment for the user. Individuals with developmental disabilities often experience joy when selecting a social event and hearing the associated music.
FoodFun LIS leverages its competitive edge by integrating entertainment into its software product. This strategy creates interest and joy during software use, encouraging increased usage and overall program effectiveness. FoodFun believes that when students enjoy an activity, they are more likely to willingly engage with the product.
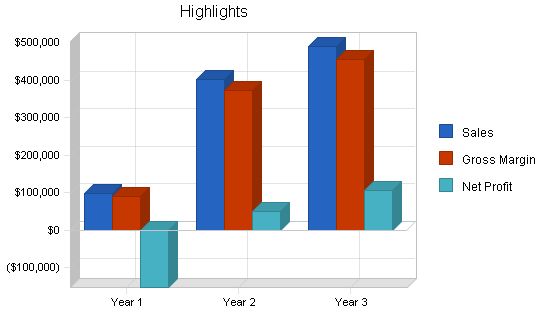
Dr. Sue Altamirankow, with a Masters and Ph.D. in special education, founded and leads FoodFun. She has eight years of teaching experience in the university setting and published a groundbreaking thesis titled "Implications in Lifeskill Training for Individuals with Autism." This thesis served as the foundation for starting the software company. Dr. Altamirankow recognized the potential to develop a study aid that is both enjoyable and effective, as it teaches vital lifeskills to individuals with developmental disabilities transitioning to a more independent life. FoodFun projects revenues of $400,397 and $490,000 for the second and third years, respectively.
1.1 Mission
Develop educational software for non-readers with developmental disabilities to enhance their independence and life skills. Our goal is to create interactive and enjoyable software that meets market demands and positively impacts society.
1.2 Keys to Success
– Create educational software that is both constructive and fun to ensure usage.
– Implement a strong marketing campaign to increase awareness among training centers, school districts, brokerages, and parents.
– Establish strict financial controls for the organization.
1.3 Objectives
– Triple sales in the first two years.
– Achieve a 20% market penetration by year four.
– Assist over 10,000 individuals with developmental disabilities.
FoodFun Lifeskills Instructional Software is a start-up organization based in Illinois. It is owned by Sue Altamirankow, a published former educator specializing in special education and autism.
2.1 Company Ownership
Sue Altamirankow founded and owns the company. Leveraging her extensive knowledge and industry contacts, Sue aims to make FoodFun LIS a success.
2.2 Start-up Summary
The formation and start of operations for FoodFun LIS will require the following assets and professional services:
– Legal services for company formation.
– Accounting services to set up QuickBooks Pro software for the company’s accounting.
– Three computer programmers to expedite software development.
– Eight computer workstations, including one server, with Microsoft Office and QuickBooks Pro software. Three networked laser printers.
– Broadband Internet connection.
– Office cubicle furniture for seven employees.
– Extension telephone system for seven.
– Copier and fax machine.
– Lunch room furniture and appliances, including a refrigerator and microwave.
– Shipping materials, including boxes and scales.
– Promotional materials.
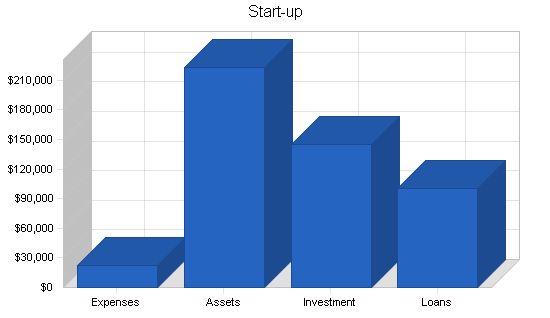
Start-up Funding:
Start-up Expenses to Fund: $22,500
Start-up Assets to Fund: $222,500
Total Funding Required: $245,000
Assets:
Non-cash Assets from Start-up: $9,000
Cash Requirements from Start-up: $213,500
Additional Cash Raised: $0
Cash Balance on Starting Date: $213,500
Total Assets: $222,500
Liabilities and Capital:
Liabilities:
Current Borrowing: $0
Long-term Liabilities: $100,000
Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills): $0
Other Current Liabilities (interest-free): $0
Total Liabilities: $100,000
Capital:
Planned Investment:
Investor 1: $60,000
Investor 2: $50,000
Other: $35,000
Additional Investment Requirement: $0
Total Planned Investment: $145,000
Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses): ($22,500)
Total Capital: $122,500
Total Capital and Liabilities: $222,500
Total Funding: $245,000
Start-up Requirements:
Start-up Expenses:
Legal: $3,000
Accounting: $2,000
Brochures: $2,500
Consultants: $0
Insurance: $0
Rent: $0
Research and Development: $0
Expensed Equipment: $15,000
Other: $0
Total Start-up Expenses: $22,500
Start-up Assets:
Cash Required: $213,500
Start-up Inventory: $0
Other Current Assets: $0
Long-term Assets: $9,000
Total Assets: $222,500
Total Requirements: $245,000
Products
FoodFun LIS’ flagship product is a software package designed for non-readers, particularly individuals with autism and developmental disabilities. The software focuses on food/cooking/nutrition and social interaction/leisure, two key areas of independent living.
Non-readers rely on visual images as a form of communication, replacing text. The software features a digital cookbook with pictures of ingredients. These pictures can be printed and taken to the grocery store. Each picture is accompanied by text with the item description. The software also includes printable utensils and pots needed for each recipe. The goal is to facilitate independent grocery shopping.
The software also includes a social occasion/party planning module. This module allows users to plan various events and provides food preparation steps for each event. It enhances socialization skills and prevents isolation.
FoodFun’s software product combines food preparation and social leisure, promoting independence and socialization for individuals with developmental disabilities. The software will be developed by three contract programmers and will be upgraded yearly.
Market Analysis Summary
The market for lifeskills training software can be segmented into four groups: centers for independent living, school districts, proactive parents, and special education administration agencies. Each segment has different communication methods and is a main purchaser of products for individuals with developmental disabilities.
The software industry for individuals with developmental disabilities is growing, with an increase in computers in classrooms. Competition includes products with printed pictures, but they lack interactivity.
Market Segmentation:
FoodFun LIS has identified four distinct market segments for their products:
1. Centers for Independent Living:
– Not-for-profit entities that assist individuals with developmental disabilities
– Offer a wide range of lifeskills training
2. School Districts:
– Required to provide appropriate education until individuals turn 21
– Consumers of lifeskills training products
3. Proactive Parents:
– Parents taking an active role in their child’s education and lifeskills training
– Willing to purchase software for home use
4. Agencies:
– Set up by states to dispense money from the state to service providers for individuals in need, often due to lawsuits
Overall, FoodFun’s software product meets the needs of these market segments, providing essential training and promoting independence for individuals with developmental disabilities.
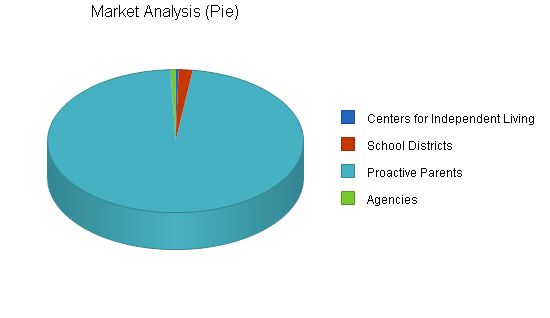
Market Analysis:
Potential Customers Growth Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 CAGR
Centers for Independent Living 6% 3,245 3,440 3,646 3,865 4,097 6.00%
School Districts 5% 14,856 15,599 16,379 17,198 18,058 5.00%
Proactive Parents 8% 824,555 890,519 961,761 1,038,702 1,121,798 8.00%
Agencies 6% 5,354 5,675 6,016 6,377 6,760 6.00%
Total 7.93% 848,010 915,233 987,802 1,066,142 1,150,713 7.93%
Target Market Segment Strategy:
Four target segments were chosen due to their likelihood of purchasing FoodFun’s products:
– Centers for Independent Living typically buy aids for teaching skills to their clients.
– School Districts use instructional tools to assist in teaching students.
– Proactive Parents seek useful devices for their child’s education at home.
– Agencies have budgets to spend on students’ education/training.
There are companies making products for individuals with developmental disabilities. Most specialize in such products. Different product groups and specific disability products exist.
Competition and Buying Patterns:
Three main companies are direct competitors to FoodFun Lifeskills Instructional Software, focusing on individuals with developmental disabilities or autism:
– WordWise makes picture-based language programs, picture cards, and community success CDs.
– Edbydesign.com offers sentence maker, match maker, counting, and sorting programs.
– Autismcoach.com’s software strengthens core cognitive skills.
Strategy and Implementation Summary:
FoodFun LIS combines education and entertainment in its software. Competitors mostly focus on skill development, whereas FoodFun makes learning fun.
FoodFun’s marketing strategy is aimed at raising product visibility among decision makers. The campaign will target these people/organizations to create awareness of available options and the benefits of FoodFun’s software.
Sales Strategy:
FoodFun will use conference participation and target cold calling to generate sales. Industry conferences and networking opportunities will be utilized. Key decision makers, such as autism consultants for school districts, will be contacted to introduce them to FoodFun’s products.
The following table and charts present monthly and yearly sales projections. Forecasts have been conservatively estimated. Sales have been broken down by customer group.
A fulfillment house will handle production, packaging, and shipping of the hard copy software product. Download options will be available to reduce costs.
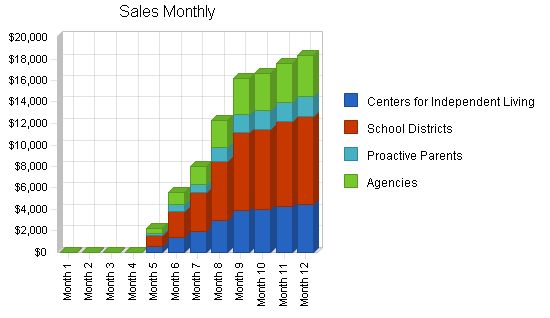
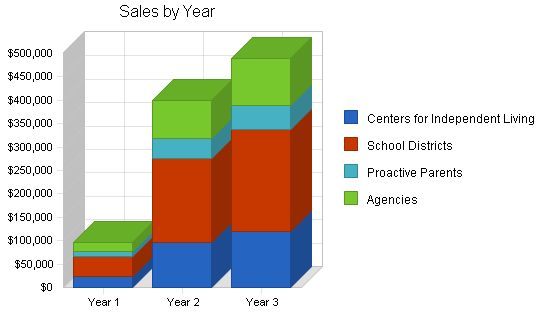
Sales Forecast
| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Centers for Independent Living | $23,439 | $96,957 | $118,616 |
| School Districts | $43,405 | $179,550 | $219,660 |
| Proactive Parents | $9,983 | $41,297 | $50,522 |
| Agencies | $19,966 | $82,593 | $101,044 |
| Total Sales | $96,793 | $400,397 | $489,842 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Centers for Independent Living | $1,641 | $6,787 | $8,303 |
| School Districts | $3,038 | $12,569 | $15,376 |
| Proactive Parents | $699 | $2,891 | $3,537 |
| Agencies | $1,398 | $5,782 | $7,073 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $6,776 | $28,028 | $34,289 |
5.4 Milestones
FoodFun LIS has several milestones, presented in the following table and chart, which will be instrumental in the organization’s success.
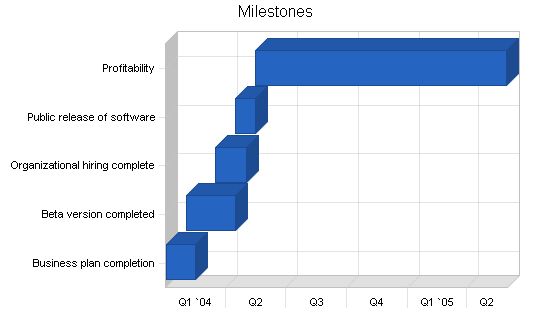
Milestones:
| Business plan completion | 1/1/2004 | 2/15/2004 | $0 | Sue | Business Development |
| Beta version completed | 2/1/2004 | 4/15/2004 | $0 | ABC | Programming |
| Organizational hiring complete | 3/15/2004 | 5/1/2004 | $0 | Sue | HR |
| Public release of software | 4/15/2004 | 5/15/2004 | $0 | ABC | Programming |
| Profitability | 5/15/2004 | 5/30/2005 | $0 | Sue | Accounting |
| Totals | $0 |
Web Plan Summary:
FoodFun will develop a website for marketing and sales purposes. Interested parties can access the site to learn more about the company and its products. Once the beta version of the software is ready, customers can download a trial version for evaluation. The website will also provide contact information for inquiries.
Online sales will be handled by a third-party internet sales business, such as Yahoo! Shopping. Customers will have the option to purchase and download the software.
Website Marketing Strategy:
The website will be marketed by including the URL in all promotional activities. This is important because it allows interested parties to view software screenshots and download the trial version. Additionally, FoodFun will rely on search engine submission for marketing. Interested parties searching for keywords related to autism software will find the website in the search results.
Development Requirements:
FoodFun will hire a computer science student to design and develop the website. Development will occur simultaneously with software development.
Management Summary:
FoodFun LIS is founded and led by Sue Altamirankow. Sue has a background in special education with a focus on autism. She has extensive knowledge and experience in the field. Sue taught at Northwestern University for eight years and was also involved in various nonprofit agencies. She decided to start FoodFun LIS to serve individuals with developmental disabilities. She took business courses to acquire the necessary skills and came up with the idea for educational and entertaining software. This marked the beginning of FoodFun Lifeskills Instructional Software.
Personnel Plan:
FoodFun LIS will require the following employees:
– Sue: HR, business development, product development, finance
– Accounting: accounting clerk
– Software development: two employees for manuals, instructions, bug updates, and version upgrades
– Marketing Sales: two employees for generating sales
– Customer Service: two employees for addressing customer inquiries and technical difficulties
| Total People | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Total Payroll | $167,000 | $225,200 | $229,200 |
Hello!
I’m Andrew Brooks, a seasoned finance consultant from the USA and the mind behind phonenumber247.com.
My career is built on a foundation of helping individuals and businesses thrive financially in an ever-changing economic landscape. At phonenumber247.com, my aim is to demystify the complex world of finance, providing clear, actionable advice that can help you navigate your financial journey with confidence. Whether it’s personal finance management, investment strategies, or understanding the nuances of market dynamics, I’m here to share insights and tools that can propel you towards your financial goals.
Welcome to my digital space, where every piece of advice is a step closer to financial clarity and success!
