ScholarshipAssist helps college-bound students search for scholarship money. ScholarshipAssist can increase award amounts for students with scholarships or improve the chances of receiving a scholarship for those on the border line. ScholarshipAssist maintains an extensive database of scholarships and offers individualized consulting.
Keys to Success:
ScholarshipAssist has three keys to success. First, it must provide significant value to customers. Second, it must maintain a 60% success rate for securing scholarships or increasing the scholarship amount. Third, it must adhere to strict financial controls.
The Market:
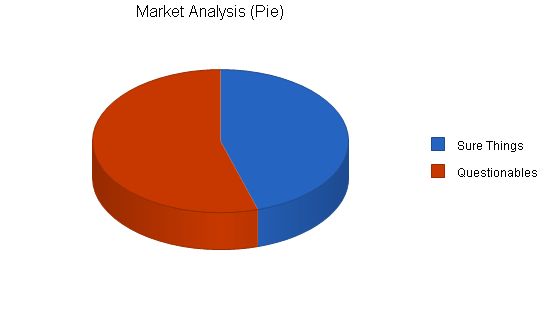
ScholarshipAssist has two market segments. The first group is sure thing applicants, who are very likely to receive scholarships. This segment is growing at 10% per year and has 93,000 potential customers. The second group is questionables, who can significantly increase their chances of getting a scholarship with ScholarshipAssist’s guidance. This group has an annual growth rate of 11% with 112,000 potential people.
Management:
ScholarshipAssist is led by industry veteran Steve Tracker, who has a graduate degree in business from Babson College. He has worked in the financial aid department at Babson College, Fannie Mae, and Pew Charitable Trust Foundation. Steve’s experience will help ensure success for ScholarshipAssist.
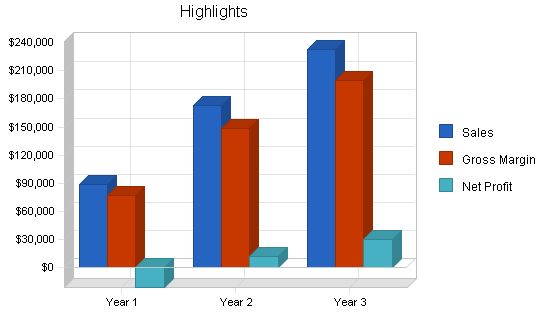
ScholarshipAssist forecasts sales of $172,589 for year two and $232,508 by year three. Profitability will also increase during this time. With an innovative business plan, a growing market, and a seasoned manager, ScholarshipAssist will quickly gain market share.
The mission of ScholarshipAssist is to help college students find scholarships and realize their dream of attending college. The company aims to maintain 100% customer satisfaction.
Objectives:
1. Become THE resource for scholarship assistance.
2. Achieve profitability within one year.
3. Generate yearly sales of $200,000 within three years.
Keys to Success:
1. Offer value to clients by providing a comprehensive database of scholarships and application information.
2. Help at least 60% of clients secure significant scholarships.
3. Maintain strict financial controls.
ScholarshipAssist was founded on the belief that there are many scholarships available to students that are not widely known. The company aims to generate profit while helping clients make college a reality. Boston has been chosen as the headquarters due to the large number of students in the area, including Tufts, MIT, Harvard, Boston College, and the University of Massachusetts.
Company Ownership:
ScholarshipAssist is a Massachusetts L.L.C. with Steve Tracker as the main shareholder.
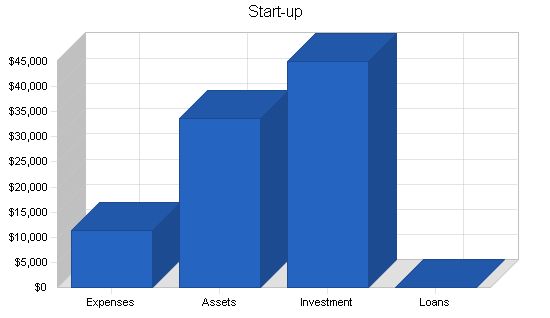
Start-up Summary:
ScholarshipAssist requires the following start-up equipment/expenses:
1. Office furniture for four workspaces, including desk, chair, light, and computer.
2. Computer server with laser printer, broadband Internet connection, and fax machine.
3. Furniture for the waiting room.
4. Legal consultation for business organization formation and contract review.
5. Business consultation, covering various areas from HR to marketing.
ScholarshipAssist offers college scholarship assistance to students. There are many scholarships available that can make college affordable.
Scholarships do not require repayment, unlike loans. They are essentially gifts. Most scholarships have prerequisites and performance requirements for recipients while they are in school.
Some scholarships have initial prerequisites like financial need, aptitude or scholastic performance, ethnicity, or association membership. Many scholarships also have performance benchmarks that must be met while the applicant is receiving aid, such as maintaining a certain grade point average.
Each organization that offers scholarships has its own requirements, which are determined by the organization.
There are thousands of scholarships available that potential applicants may not be aware of. This is where ScholarshipAssist comes in. They provide clients with a list of possible scholarships from their database, which is continually updated. They also help increase the likelihood of a client receiving a scholarship by providing individualized suggestions.
ScholarshipAssist uses a fee structure based on incentivized performance. They only get paid if they successfully help the client realize a scholarship. This encourages potential customers to sign up, as payment is contingent on their success.
ScholarshipAssist has identified two customer segments: "sure thing" customers who are likely to get a scholarship, and "questionables" who need assistance to secure a scholarship. Career services personnel at high schools and colleges usually assist these segments, but their time and resources are limited. There are no direct competitors for ScholarshipAssist’s services.
ScholarshipAssist has segmented the market into two distinct groups. "Sure thing" customers have high SAT scores or high household incomes and are knowledgeable about the college education process. "Questionables" have SAT scores below a certain threshold, need-based financial aid, and recognize the need for assistance in securing a scholarship.
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5
Potential Customers Growth CAGR
Sure Things 93,098 102,408 112,649 123,914 136,305 10%
Questionables 112,343 124,139 137,174 151,577 167,493 10.5%
Total 205,441 226,547 249,823 275,491 303,798 10.27%
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy:
ScholarshipAssist will use the same media outlets for its advertising campaign, but tailored ads for different segments. Some ads highlight ScholarshipAssist’s ability to secure larger scholarship amounts, appealing to students likely to receive a scholarship.
4.3 Service Business Analysis:
The scholarship assistance industry is currently small, with most help coming from career service counselors at schools. Some firms provide scholarship databases online, but lack individualized assistance.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns:
While ScholarshipAssist doesn’t have direct competition, there are other companies in the same space:
– Guidance school counselors provide similar services.
– Internet-based databases offer lists of scholarships.
– Individual consultants offer one-on-one services, but are expensive for most students.
Students prioritize affordability when choosing a service. ScholarshipAssist charges fees only if they succeed.
Strategy and Implementation Summary:
ScholarshipAssist’s strategy is to raise awareness and educate clients about their effective services. The marketing campaign focuses on the extensive database and individualized counseling. The sales strategy aims to convert leads into customers by providing scholarships for students who wouldn’t receive any or increasing awards for others.
5.1 Competitive Edge:
ScholarshipAssist’s competitive edge is its effectiveness in securing scholarships and increasing award amounts. With a 60% success rate based on extensive research and industry knowledge, they understand how to win scholarships for students.
5.2 Marketing Strategy:
ScholarshipAssist’s marketing strategy aims to raise awareness and demonstrate value to student target groups. Advertisements in local magazines highlight the ability to secure larger awards. A grass roots campaign includes a referral system and student representatives to spread the message.
5.3 Sales Strategy:
The sales campaign aims to convert qualified leads into paying customers. ScholarshipAssist’s high success rate and no-risk policy make the conversion process easier. Students can use other services and only pay if they receive a scholarship.
5.3.1 Sales Forecast:
Initial sales will be slow due to the start-up phase and the seasonal nature of scholarship applications. ScholarshipAssist receives a 6% commission on scholarships obtained, providing an incentive to raise more money for students. The forecasts are conservative but benefit from a large student market and increasing demand for assistance.
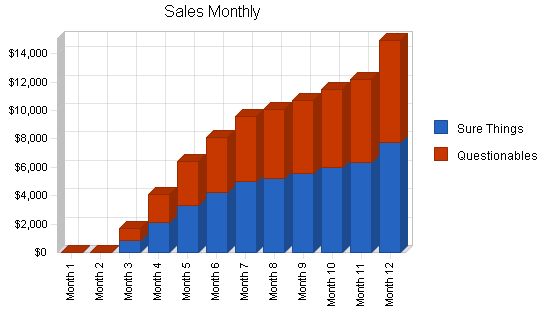
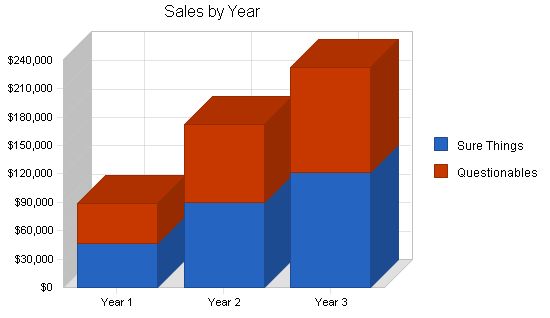
Sales Forecast:
Sure Things:
Year 1: $46,454
Year 2: $89,890
Year 3: $121,098
Questionables:
Year 1: $42,738
Year 2: $82,699
Year 3: $111,410
Total Sales:
Year 1: $89,192
Year 2: $172,589
Year 3: $232,508
Direct Cost of Sales:
Sure Things:
Year 1: $6,504
Year 2: $12,585
Year 3: $16,954
Questionables:
Year 1: $5,983
Year 2: $11,578
Year 3: $15,597
Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales:
Year 1: $12,487
Year 2: $24,162
Year 3: $32,551
5.4 Milestones:
1. Completion of business plan
2. Profitability
3. Monthly revenue exceeding $15,000
Milestones:
Milestone Start Date End Date Budget Manager Department
Completion of business plan 1/1/2003 2/15/2003 $0 Steve Strategic
Profitability 1/1/2003 9/30/2003 $0 Steve Operations
Monthly rev $15,000 1/1/2003 2/1/2004 $0 Steve Operations
Totals $0
Web Plan Summary:
ScholarshipAssist will have a website to disseminate information to prospective customers. A website is a cost-effective means of broadcasting information that allows people to browse at their own leisure. It also allows them to find answers to their questions without help from ScholarshipAssist. The site will showcase services, case studies, and accomplishments.
6.1 Website Marketing Strategy:
ScholarshipAssist will work to increase traffic on the website by referencing it in printed materials and through diligent website submission. This will ensure that students looking for these services will find ScholarshipAssist.
6.2 Development Requirements:
The site will be developed by M.I.T. computer science students who work at below market rates.
Management Summary:
Steve Tracker, the founder and president, brings a wealth of skills and experience to ScholarshipAssist. He received his undergraduate and graduate degrees at Babson College and worked at Babson in their financial aid department for two years. He then worked at Fannie Mae as a project manager and at the Pew Charitable Trust Foundation for six years, learning about scholarship awards.
7.1 Personnel Plan:
ScholarshipAssist will need a total of four employees. The following chart provides financial information regarding the personnel plan:
– Steve: operations, marketing, some financials, business development
– Researcher: development and maintenance of the scholarship database
– Account manager (2): responsible for interactions with clients
Year 1:
– Steve: $24,000
– Researcher: $16,500
– Account Manager: $13,500
– Account Manager: $13,500
Total people: 4
Total payroll: $67,500
This section will outline important financial information.
8.1 Important Assumptions:
This table details important financial assumptions.
General Assumptions:
Year 1: 1, Year 2: 2, Year 3: 3
Current Interest Rate: 10.00%
Long-term Interest Rate: 10.00%
Tax Rate: 30.00%
Other: 0
8.2 Break-even Analysis:
The Break-even Analysis is shown below.
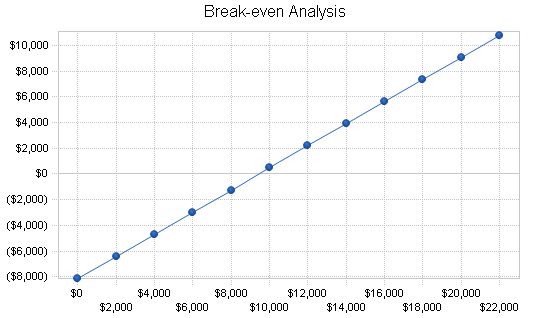
Break-even Analysis
Monthly Revenue Break-even: $9,460
Assumptions:
– Average Percent Variable Cost: 14%
– Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost: $8,136
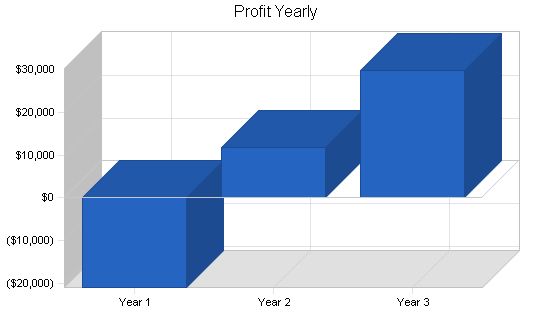
8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
The table below shows the Projected Profit and Loss.
Pro Forma Profit and Loss
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Sales | $89,192 | $172,589 | $232,508 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $12,487 | $24,162 | $32,551 |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $12,487 | $24,162 | $32,551 |
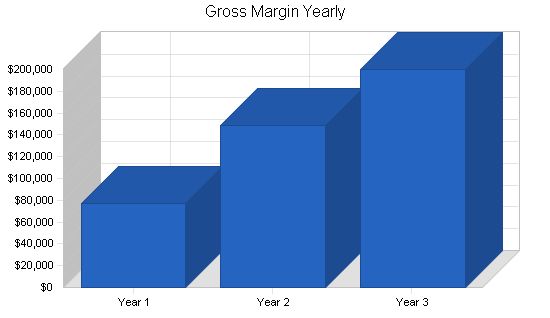
| Gross Margin | $76,705 | $148,426 | $199,957 |
| Gross Margin % | 86.00% | 86.00% | 86.00% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $67,500 | $96,000 | $118,000 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $4,200 | $5,500 | $6,000 |
| Depreciation | $2,004 | $2,004 | $2,004 |
| Rent | $7,200 | $7,200 | $7,200 |
| Utilities | $2,400 | $2,400 | $2,400 |
| Insurance | $2,400 | $2,400 | $2,400 |
| Payroll Taxes | $10,125 | $14,400 | $17,700 |
| Other | $1,800 | $1,800 | $1,800 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $97,629 | $131,704 | $157,504 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($20,924) | $16,722 | $42,453 |
| EBITDA | ($18,920) | $18,726 | $44,457 |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Taxes Incurred | $0 | $5,017 | $12,736 |
| Net Profit | ($20,924) | $11,706 | $29,717 |
| Net Profit/Sales | -23.46% | 6.78% | 12.78% |
8.4 Projected Cash Flow
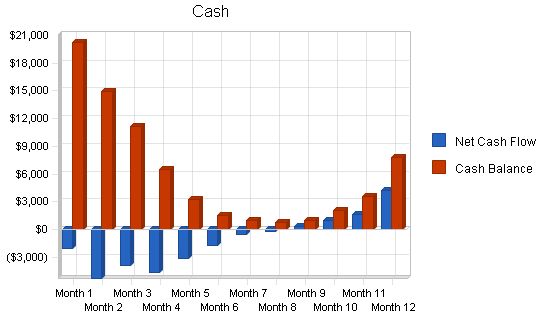
The following table and chart indicate Projected Cash Flow.
Pro Forma Cash Flow:
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Sales | $89,192 | $172,589 | $232,508 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $89,192 | $172,589 | $232,508 |
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $89,192 | $172,589 | $232,508 |
| Expenditures | |||
| Cash Spending | $67,500 | $96,000 | $118,000 |
| Bill Payments | $36,201 | $62,122 | $81,151 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $103,701 | $158,122 | $199,151 |
| Net Cash Flow | ($14,509) | $14,467 | $33,357 |
| Cash Balance | $7,841 | $22,308 | $55,665 |
Projected Balance Sheet:
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash | $7,841 | $22,308 | $55,665 |
| Other Current Assets | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 |
| Total Current Assets | $9,141 | $23,608 | $56,965 |
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $2,004 | $4,008 | $6,012 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $7,996 | $5,992 | $3,988 |
| Total Assets | $17,137 | $29,600 | $60,953 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $4,411 | $5,168 | $6,804 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $4,411 | $5,168 | $6,804 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $4,411 | $5,168 | $6,804 |
| Paid-in Capital | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($11,350) | ($32,274) | ($20,568) |
| Earnings | ($20,924) | $11,706 | $29,717 |
| Total Capital | $12,726 | $24,432 | $54,149 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $17,137 | $29,600 | $60,953 |
| Net Worth | $12,726 | $24,432 | $54,149 |
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 93.50% | 34.72% | 8.15% |
| Other Current Assets | 7.59% | 4.39% | 2.13% | 35.03% |
| Total Current Assets | 53.34% | 79.76% | 93.46% | 55.79% |
| Long-term Assets | 46.66% | 20.24% | 6.54% | 44.21% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 25.74% | 17.46% | 11.16% | 25.11% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 22.00% |
| Total Liabilities | 25.74% | 17.46% | 11.16% | 47.11% |
| Net Worth | 74.26% | 82.54% | 88.84% | 52.89% |
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 86.00% | 86.00% | 86.00% | 100.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 109.46% | 79.22% | 73.22% | 77.99% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.85% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | -23.46% | 9.69% | 18.26% | 3.35% |
| Current | 2.07 | 4.57 | 8.37 | 1.73 |
| Quick | 2.07 | 4.57 | 8.37 | 1.30 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 25.74% | 17.46% | 11.16% | 59.92% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | -164.42% | 68.45% | 78.40% | 6.16% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | -122.10% | 56.50% | 69.65% | 15.38% |
| Net Profit Margin | -23.46% | 6.78% | 12.78% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | -164.42% | 47.91% | 54.88% | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 9.21 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 28 | 26 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 5.20 | 5.83 | 3.81 | n.a |
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.13 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | n.a |
| Net Working Capital | $4,730 | $18,440 | $50,161 | n.aGeneral Assumptions:
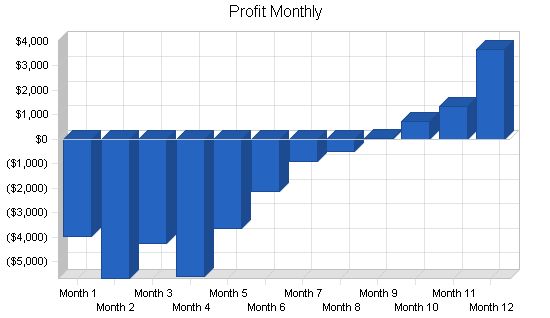
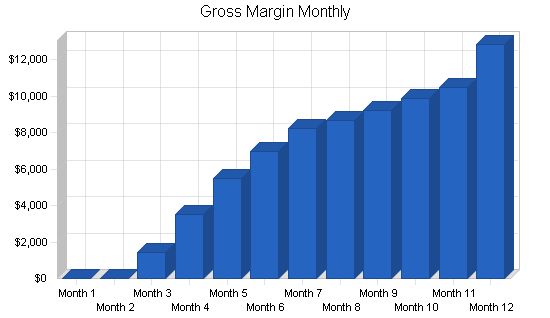
Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Plan Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Current Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Long-term Interest Rate 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% 10.00% Tax Rate 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% 30.00% Other 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Pro Forma Profit and Loss: Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Sales $0 $0 $1,686 $4,093 $6,380 $8,129 $9,579 $10,049 $10,685 $11,499 $12,179 $14,913 Direct Cost of Sales $0 $0 $236 $573 $893 $1,138 $1,341 $1,407 $1,496 $1,610 $1,705 $2,088 Other Costs of Sales $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 Total Cost of Sales $0 $0 $236 $573 $893 $1,138 $1,341 $1,407 $1,496 $1,610 $1,705 $2,088 Gross Margin $0 $0 $1,450 $3,520 $5,487 $6,991 $8,238 $8,642 $9,189 $9,889 $10,474 $12,825 Gross Margin % 0.00% 0.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% 86.00% Expenses Payroll $2,000 $3,500 $3,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 $6,500 Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 $350 Depreciation $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 $167 Rent $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 Utilities $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 Insurance $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 Payroll Taxes 15% $300 $525 $525 $975 $975 $975 $975 $975 $975 $975 $975 $975 Other $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 $150 Total Operating Expenses $3,967 $5,692 $5,692 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 $9,142 Profit Before Interest and Taxes ($3,967) ($5,692) ($4,242) ($5,622) ($3,655) ($2,151) ($904) ($500) $47 $747 $1,332 $3,683 EBITDA ($3,800) ($5,525) ($4,075) ($5,455) ($3,488) ($1,984) ($737) ($333) $214 $914 $1,499 $3,850 Interest Expense $0 $0 $0 $0 $0 $ Pro Forma Balance Sheet |
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $22,350 | $20,290 | $14,983 | $11,135 | $6,442 | $3,263 | $1,516 | $975 | $706 | $1,006 | $2,030 | $3,621 | $7,841 |
| Other Current Assets | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,300 |
| Total Current Assets | $23,650 | $21,590 | $16,283 | $12,435 | $7,742 | $4,563 | $2,816 | $2,275 | $2,006 | $2,306 | $3,330 | $4,921 | $9,141 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 | $10,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $167 | $334 | $501 | $668 | $835 | $1,002 | $1,169 | $1,336 | $1,503 | $1,670 | $1,837 | $2,004 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $10,000 | $9,833 | $9,666 | $9,499 | $9,332 | $9,165 | $8,998 | $8,831 | $8,664 | $8,497 | $8,330 | $8,163 | $7,996 |
| Total Assets | $33,650 | $31,423 | $25,949 | $21,934 | $17,074 | $13,728 | $11,814 | $11,106 | $10,670 | $10,803 | $11,660 | $13,084 | $17,137 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $1,740 | $1,958 | $2,186 | $2,946 | $3,256 | $3,493 | $3,689 | $3,753 | $3,839 | $3,949 | $4,041 | $4,411 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $1,740 | $1,958 | $2,186 | $2,946 | $3,256 | $3,493 | $3,689 | $3,753 | $3,839 | $3,949 | $4,041 | $4,411 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 | $1,740 | $1,958 | $2,186 | $2,946 | $3,256 | $3,493 | $3,689 | $3,753 | $3,839 | $3,949 | $4,041 | $4,411 |
| Paid-in Capital | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $45,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) | ($11,350) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($3,967) | ($9,659) | ($13,901) | ($19,523) | ($23,178) | ($25,329) | ($26,233) | ($26,733) | ($26,686) | ($25,939) | ($24,607) | ($20,924) |
| Total Capital | $33,650 | $29,683 | $23,991 | $19,749 | $14,127 | $10,472 | $8,321 | $7,417 | $6,917 |
Hello!
I’m Andrew Brooks, a seasoned finance consultant from the USA and the mind behind phonenumber247.com.
My career is built on a foundation of helping individuals and businesses thrive financially in an ever-changing economic landscape. At phonenumber247.com, my aim is to demystify the complex world of finance, providing clear, actionable advice that can help you navigate your financial journey with confidence. Whether it’s personal finance management, investment strategies, or understanding the nuances of market dynamics, I’m here to share insights and tools that can propel you towards your financial goals.
Welcome to my digital space, where every piece of advice is a step closer to financial clarity and success!
